If you’ve spent time building your own AI-powered agents, you’ve almost certainly run into both LangChain and LlamaIndex. These frameworks have become the go-to options for developers building AI agents, and for good reason. That said, something often gets overlooked. According to Zapier’s 2025 survey of over 500 enterprise leaders, 78% of enterprises are struggling to integrate AI with existing systems. Most prototypes never push past production. Much of that friction starts with picking the wrong framework. So, let’s change that. Our LangChain vs LlamaIndex comparison is here to help you decide which framework better powers your AI agent.
What Are These Frameworks, Anyway?
Before diving into the head-to-head, it helps to understand what each tool is actually trying to do, because they don’t have identical goals. Treating them as interchangeable alternatives is one of the most common mistakes developers make early in a project, and it often leads to unnecessary rewrites later.
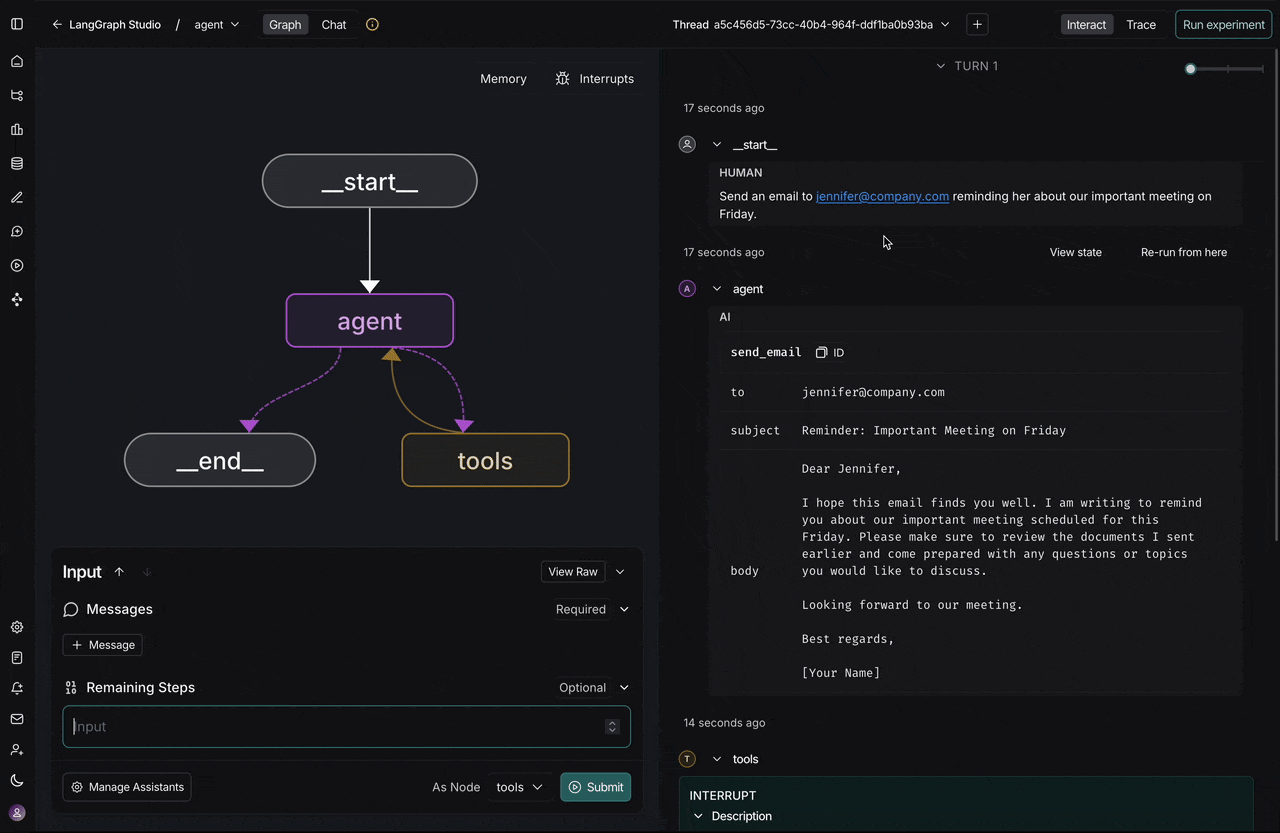
LangChain launched in October 2022 and quickly became the most recognizable LLM application framework in the ecosystem. It’s built around a chain-based, modular architecture that lets you link prompts, models, memory, tools, and agents into multi-step workflows. It’s a general-purpose toolkit for LLM development—versatile and powerful when you need depth.
The LangChain team has since introduced LangGraph as the primary way to build agentic workflows within the ecosystem, giving developers a stateful, graph-based approach to orchestration with features like time-travel debugging and human-in-the-loop support.
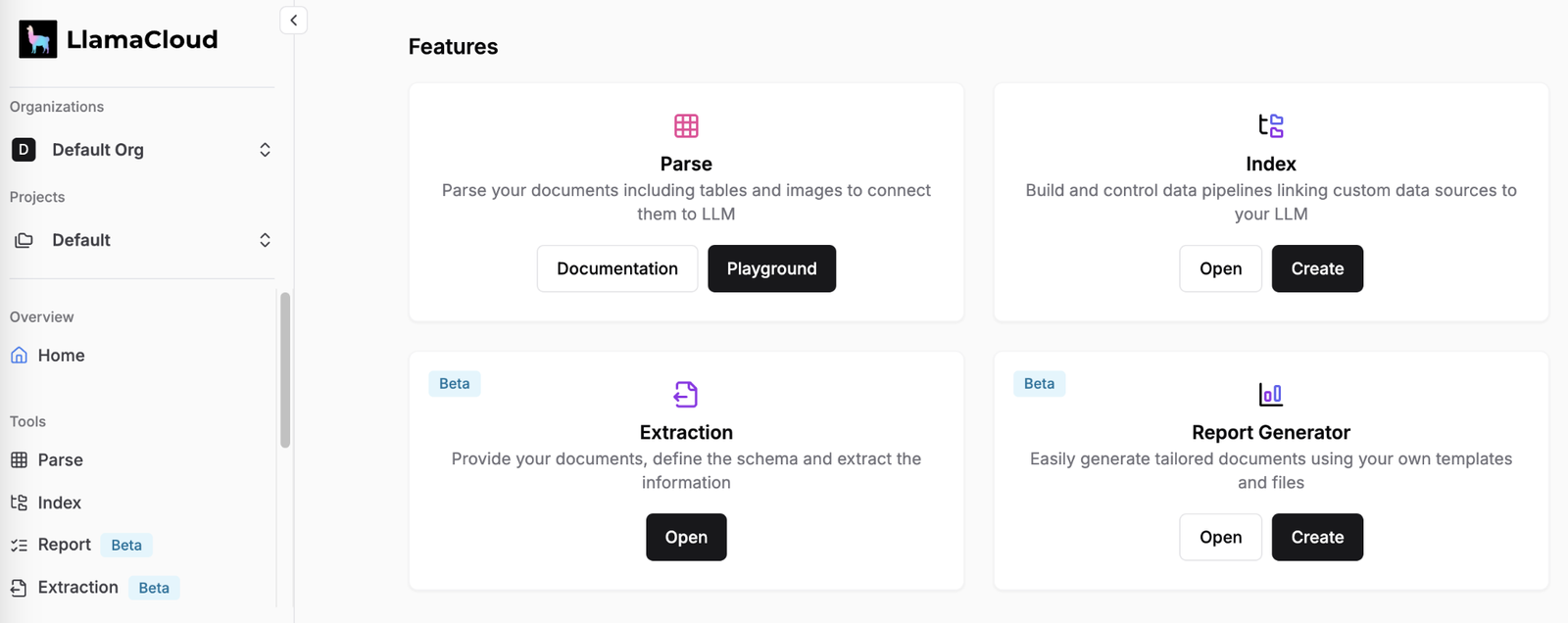
LlamaIndex, originally launched as GPT Index in November 2022, took a different path. Rather than trying to be everything to everyone, it zeroed in on data retrieval and indexing. It’s purpose-built for connecting LLMs to external data sources through retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and it does that job extremely well.
With over 44,000 GitHub stars and 300-plus data connectors through LlamaHub, it has grown into the default choice for document-heavy, data-centric applications. It’s also worth noting that LlamaIndex has built out its own agentic capabilities in recent years, so writing it off as just a “retrieval tool” would be selling it short.
LangChain vs LlamaIndex – How They Think About Agents
The architectural differences between these two frameworks are real, and they matter a lot when you’re deciding which one to build on.
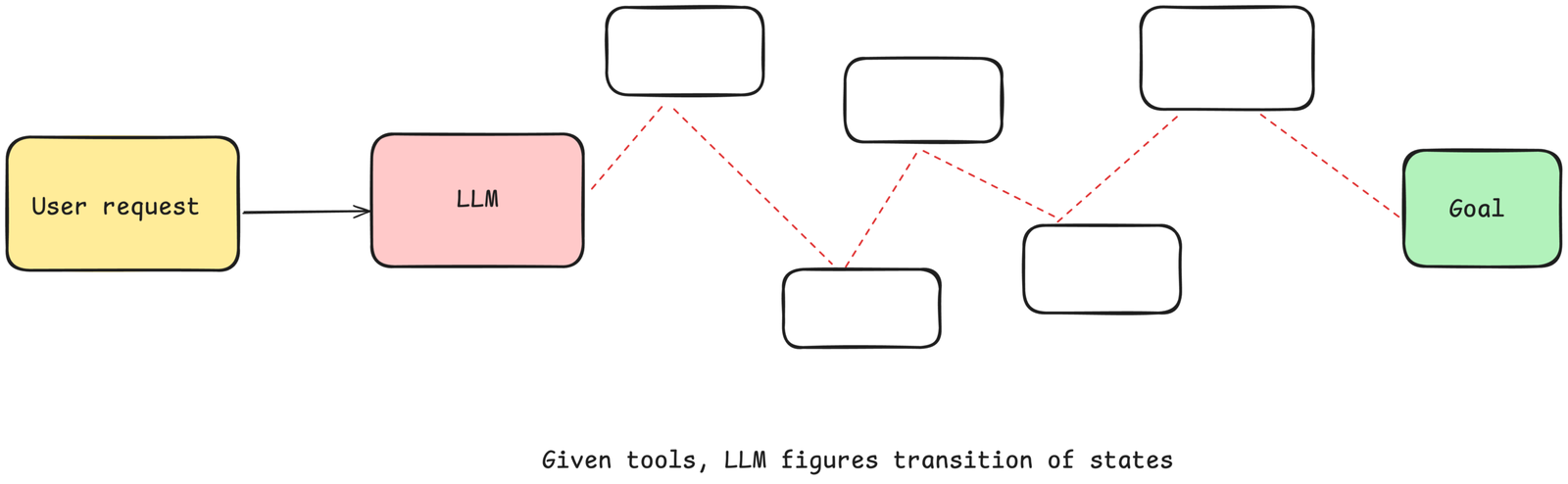
LangChain’s agent system is built around dynamic tool selection. Agents observe the environment, decide which tools to invoke (APIs, databases, search engines, etc.), and loop through a reasoning process until they produce a final answer. This makes it especially suited for open-ended, multi-step tasks where the agent needs to adapt in real time. LangGraph extends this further by adding stateful graph abstractions with proper checkpointing, parallel branches, and async support.
LlamaIndex, by contrast, approaches agent orchestration through its Workflows module, which is an event-driven, async-first system. Developers define steps using clean Python decorators, and state flows explicitly through a Context API rather than being implied by a global graph. This makes LlamaIndex agents arguably easier to reason about, especially for teams that want predictable behavior in data retrieval pipelines. One key trade-off: default LlamaIndex workflows are stateless, meaning you have to manage persistence yourself unless you plug in additional tooling.
LangChain vs LlamaIndex – Feature-by-Feature Comparison
| </> | LangChain | LlamaIndex |
| Primary Use Case | Complex multi-step agents, diverse AI workflows | RAG, document Q&A, data-heavy applications |
| Orchestration Style | Graph/state machine (LangGraph) | Event-driven Workflows |
| RAG Capabilities | Modular, customizable retrieval chains | Built-in, mature RAG modules |
| Developer Experience | Steeper curve; operator overloading in LangGraph | Clean Python abstractions; easier onboarding |
| Observability | LangSmith (evaluation, tracing, monitoring) | Third-party integrations (Arize, W&B, etc.) |
| Ecosystem Size | Larger; most GitHub stars and integrations | 300+ connectors via LlamaHub |
| Memory Management | Short and long-term memory utilities | SQLite or vector-based chat history |
| Stateful Agents | Built-in with checkpointing in LangGraph | Via explicit Context API |
| Open Source License | MIT | MIT |
| Pricing (Hosted) | LangSmith/Platform pricing varies | Free tier, $50/mo (Starter), $500/mo (Pro) |
LangChain with LangGraph is built for complex, multi-step AI agents that need strong orchestration, state management, and deep observability, while LlamaIndex is optimized for RAG, document Q&A, and data-heavy applications with faster onboarding. LangChain offers graph-based workflows, flexible retrieval customization, and built-in stateful agents, whereas LlamaIndex provides mature RAG modules, cleaner Python abstractions, and extensive data connectors through LlamaHub. Both use MIT licensing, but the hosted tooling differs, with LangSmith priced on a per-use basis and LlamaIndex offering structured paid tiers.
RAG Performance: LlamaIndex’s Home Turf
When it comes to retrieval-augmented generation, LlamaIndex is the stronger out-of-the-box option. This isn’t really a contested point. It offers built-in hybrid search that combines vector and keyword retrieval, prebuilt query engines, routers, and re-rankers, and a data ingestion pipeline that handles PDFs, Word documents, spreadsheets, and web pages while preserving document structure. That last detail matters more than it sounds: accurate retrieval often depends on preserving context and hierarchy, not just extracting raw text.
LlamaIndex also makes it remarkably easy to connect to diverse data sources. Its LlamaHub ecosystem covers everything from Notion and Google Drive to SQL databases and Slack, which means you can build a knowledge assistant over your company’s actual data without having to write a dozen custom connectors. The query interface accepts natural language prompts and returns knowledge-augmented responses, abstracting away the underlying retrieval complexity from the application layer.
LangChain can absolutely do RAG, but it requires more assembly. You’re working with modular components: text splitters, vector store integrations, retrieval chains, and so on. That modularity is a strength if you need fine-grained control over every piece of the pipeline. But if you just need to stand up a reliable document Q&A system quickly, LlamaIndex will get you there faster. For teams working in legal research, technical documentation, or any domain where retrieval precision is the primary success metric, LlamaIndex’s focused design gives it a meaningful edge.
Where LangChain Pulls Ahead
LangChain’s real strength shows up when you’re building something that goes beyond retrieval. Here are the scenarios where it genuinely earns its place:
- Complex reasoning chains: If your agent needs to gather data from multiple sources, synthesize it, and produce a structured output, LangChain’s chaining model handles this elegantly.
- Customer service automation: LangChain’s memory management and tool-calling capabilities make it well-suited for long-running, context-aware conversational agents.
- Multimodal data sources: While LlamaIndex handles images and text, LangChain’s media support is broader and extends to video data via APIs and other integrations.
- Granular control: Its brick-by-brick approach gives developers maximum control over functionality at every stage of the workflow.
- Enterprise compliance: For regulated industries, LangChain can be configured to use self-hosted LLMs, keeping sensitive data within organizational boundaries. It also supports custom memory policies, including PII redaction and data retention controls.
- Observability at scale: LangSmith provides a one-stop shop for evaluation, tracing, and monitoring that LlamaIndex doesn’t yet match with a native equivalent.
Developer Experience: Honest Observations
This is an area where opinions diverge, and a lot depends on what you’re building. LlamaIndex tends to win on first impressions. Its abstractions are more Pythonic, the setup is more straightforward, and new developers can get a working RAG prototype running in far less time. The framework handles much of the configuration complexity in the background, so you’re not fighting boilerplate before you even get to the interesting parts of your application.
LangGraph, on the other hand, introduces custom syntax and operator overloading (for example, using the pipe operator for pipeline composition) that can feel unnatural at first. It’s powerful once you’ve internalized it, but the learning curve is steeper. There’s also been consistent criticism in the community around LangChain’s deprecation cadence, with LangGraph v0.2 and v0.6 both introducing breaking changes that required users to update imports and variable names. For teams with limited bandwidth, that kind of churn is a real cost. If your team isn’t already comfortable with LangChain’s ecosystem, budgeting extra time for onboarding is the realistic move.
LlamaIndex also has growing pains, but its event-driven Workflows model has been praised for being easier to debug and extend without fighting the framework. The Context API, which makes state explicit rather than implied, also makes it much clearer what’s happening inside your agents at any given point. That transparency pays dividends during debugging and when handing off code to other team members. Documentation quality on both sides has improved substantially over the past year, so neither framework leaves you stranded, but LlamaIndex’s learning curve tends to flatten out faster for most developers.
When to Use Each (and When to Use Both)
Picking a framework isn’t always an either/or decision. Here’s a practical breakdown:
Choose LlamaIndex when:
- Your application is document-heavy (contract analysis, enterprise search, technical documentation, Q&A)
- You need fast time-to-value with a small team.
- RAG accuracy and retrieval performance are your primary concerns
- You want clean, Pythonic code that’s easy for your team to maintain
Choose LangChain / LangGraph when:
- You’re building complex, multi-step autonomous agents with dynamic tool use.
- You need robust observability and evaluation tooling (LangSmith)
- Your use case requires multimodal support or complex data structures.
- You’re already embedded in the LangChain ecosystem and want cohesion.
Use both when:
- You’re building enterprise RAG systems that also require sophisticated agent logic.
- A common pattern is using LlamaIndex for fast, accurate retrieval and LangChain for the downstream agent reasoning. This combination leverages each framework’s core strengths without forcing either one to do something it’s not optimized for.
Ecosystem and Community Health
Both frameworks are open source under MIT licenses, which means no licensing costs on top of your underlying LLM API and infrastructure spend. LangChain leads in raw GitHub metrics, with more stars, forks, and a larger contributor community built on a first-mover advantage since late 2022. Its ecosystem also extends across both Python and JavaScript, making it more accessible to full-stack teams that aren’t working in a pure Python environment. LlamaIndex’s ecosystem is more focused but deep, particularly around data connectivity. Its LlamaHub repository of connectors has become a go-to resource for developers needing to integrate diverse data sources quickly.
Both frameworks also play well with each other and with broader AI infrastructure. LlamaIndex integrates with popular tools like LangChain itself, ChatGPT plugins, vector databases (Pinecone, Weaviate, Chroma, and others), and tracing platforms. This interoperability means you’re not locked into a single philosophy, even if you pick one as your primary framework. LangChain similarly integrates with virtually every major LLM provider, including OpenAI, Anthropic, Hugging Face, Cohere, and more, which matters when you need the flexibility to swap models without rewriting your agent logic.
On the commercial side, LlamaIndex’s hosted platform uses a credit-based model with a free tier for smaller workloads, a $50/month Starter plan, and a $500/month Pro plan. LangChain’s commercial offerings center around LangSmith and the LangGraph Platform, with pricing that scales with usage and team size. Neither framework will lock you into a vendor relationship on the open-source side, which is an important consideration for teams that need flexibility down the road.
Wrapping Up
The choice between LangChain and LlamaIndex is not ideological; it’s tactical. If your agent’s primary value comes from precise retrieval, RAG over large document sets, or enterprise knowledge access, choose LlamaIndex. It is purpose-built, noticeably faster at indexing and querying, and cleaner for anything retrieval-heavy.
But if your agent needs to reason across tools, maintain complex multi-step state, self-correct, plan, or run reliably at scale with strong tracing and observability, choose LangChain—especially LangGraph.
Most serious production agents in 2025–2026 don’t pick one or the other.
They compose: LlamaIndex handles high-quality retrieval and indexing, LangChain/LangGraph handles orchestration, tool-calling loops, state, memory, and recovery.
Bottom line:
- Identify your current bottleneck.
- Start with the framework that removes that bottleneck fastest.
- Then layer the other one on top.
That’s how capable, maintainable agent systems actually get shipped.
